With Home Values Surging, Is it Still Affordable to Buy Right Now?

Housing inventory is at an all-time low. Realtor.com just reported that there are 39% fewer homes for sale today than there were last year. At the same time, buyer demand remains strong. In a recent newsletter, research analyst Ivy Zelman explained:
“Although the headwind of severe supply constraints in most markets has contributed to slight moderation in seasonally-adjusted and year-over-year new pending contract growth for two consecutive months (albeit still growing strongly), the underlying strength of buyer demand, particularly for this time of year, remains apparent.”
Whenever there’s a shortage in the supply of an item that’s in high demand, the price of that item increases. That’s exactly what’s happening in the real estate market right now. As a result, home values are surging.
This is great news if you’re planning to sell your house. On the other hand, as either a first-time or repeat buyer, this may instead seem like troubling news. Purchasers, however, should realize that the price of a house is not as important as the monthly cost. Here’s how it breaks down.
There are several factors that influence the cost of a home. Two of the major ones are:
- The price of the home
- The mortgage rate at which a buyer can borrow the funds necessary to purchase the home
How do these factors impact affordability?
The National Association of Realtors (NAR) produces a Housing Affordability Index which takes these factors into account and determines an overall affordability score for housing. According to NAR, the index:
“…measures whether or not a typical family earns enough income to qualify for a mortgage loan on a typical home at the national and regional levels based on the most recent price and income data.”
Their methodology states:
“To interpret the indices, a value of 100 means that a family with the median income has exactly enough income to qualify for a mortgage on a median-priced home. An index above 100 signifies that family earning the median income has more than enough income to qualify for a mortgage loan on a median-priced home, assuming a 20 percent down payment.”
So, the higher the index, the more affordable it is to purchase a home. Here’s a graph of the index going back to 1990: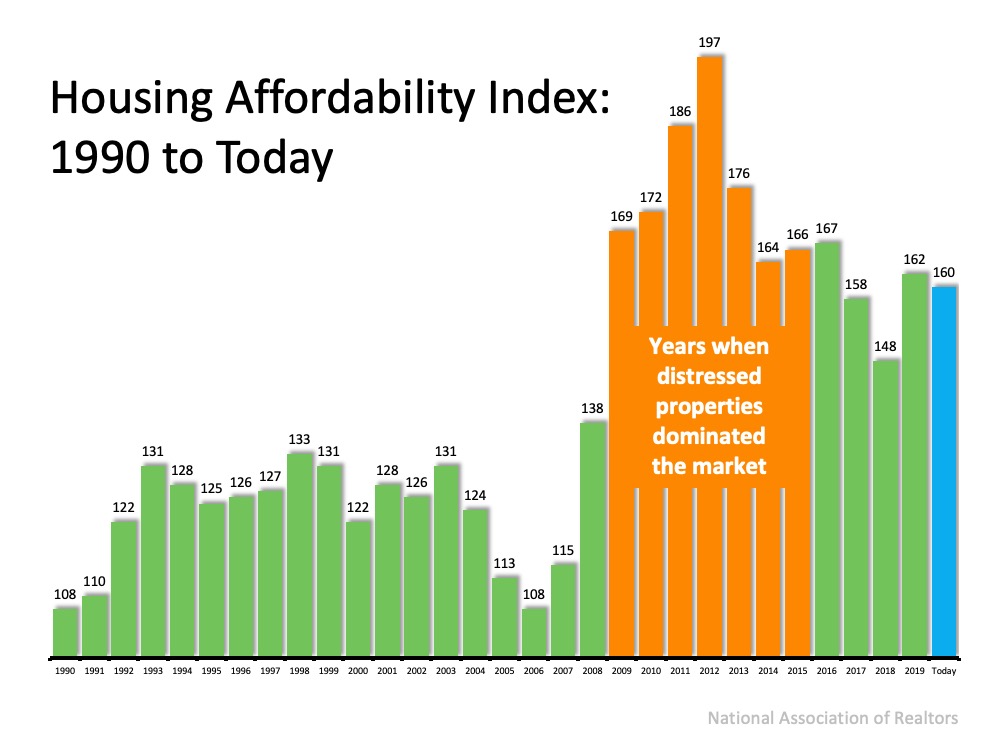 The blue bar represents today’s affordability. We can see that homes are more affordable now than they were from:
The blue bar represents today’s affordability. We can see that homes are more affordable now than they were from:
- 1990 to 2008
- 2017 to 2018
Buying a home today is just a little less affordable than it was last year, but still very affordable compared to historical housing market trends.
Note: During the housing crash from 2009 to 2015, distressed properties (foreclosures and short sales) dominated the market. Those properties were sold at large discounts not seen before in the housing market.
Why are homes still affordable today?
The number one factor impacting today’s homebuying affordability is record-low mortgage rates. There’s no doubt that prices are on the rise. However, mortgage rates have fallen dramatically. Last week, Freddie Mac announced that the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage was 2.72%. Last year at this time, the average rate was 3.68%.
If you’re considering purchasing your first home or moving up to the one you’ve always hoped for, it’s important to understand how affordability plays into the overall cost of your home. With that in mind, buying while mortgage rates are as low as they are now may save you quite a bit of money over the life of your home loan.
Bottom Line
At this point, home purchase affordability is still in a historically good place. However, we need to watch price increases going forward. As Mark Fleming, Chief Economist at First American, noted in a recent post:
“Faster nominal house price appreciation can erode, or even eliminate, the boost in affordability from lower mortgage rates, especially if household income growth doesn’t keep up.”

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link

